Introduction
The global industrial sugar market is currently experiencing significant growth, largely attributed to several key factors. One of the primary drivers is the rising demand for industrial sugar in the beverage industry worldwide. Sugar is a crucial ingredient in soft drinks, juices, and various other beverages, contributing to their taste and palatability. As consumer preferences for these products continue to grow, the industrial sugar market is poised to benefit.
The expansion of the food processing industry plays a pivotal role in propelling the market forward. Food processors rely on industrial sugar as an essential ingredient in a wide range of products, including baked goods, snacks, and processed foods. This expansion is particularly notable as the food industry constantly evolves to meet changing consumer demands and tastes.
The confectionery sector also contributes significantly to the market’s growth. Industrial sugar is a fundamental component in the production of candies, chocolates, and other sweets. The sector’s rapid growth, driven by consumer indulgence and innovation in confectionery products, further fuels the demand for industrial sugar.
Definition
Industrial sugar, also known as bulk sugar or industrial sugar, is utilised in many different industries and commands a substantial market share. Instead of being consumed directly, this highly refined sugar is mostly used for industrial applications. Due to its adaptable qualities and broad range of uses, industrial sugar is a vital component in a number of sectors and supports a booming industry.
One of the main markets for industrial sugar is the food and beverage sector. Processed foods, confections, drinks, and baked items all require it as a key component. Industrial sugar is essential to manufacturers because of its sweetness, texture, and preservation qualities, which enhance the flavour and general quality of these products. Its vast usage in the food sector is also a result of its capacity to serve as a bulking agent, stabiliser, and flavour enhancer.
Challenges in industrial sugar market
The industrial sugar market faces several challenges that impact its operations and growth prospects. These challenges include:
- Health Concerns and Sugar Reduction Trends: Increasing awareness of the health risks associated with excessive sugar consumption has led to changing consumer preferences. Many consumers are actively seeking products with lower sugar content or opting for sugar substitutes. This shift in consumer behavior can affect the demand for industrial sugar, especially in the food and beverage industry.
- Sugar Taxes and Regulatory Measures: Governments in various countries have implemented sugar taxes as a means to reduce sugar consumption and combat rising rates of obesity and related health issues. These taxes can increase the cost of sugary products, which may, in turn, reduce consumer demand for such products.
- Consumer Demand for Clean Labels: There is a growing trend among consumers to choose foods and beverages with clean labels, which means products with minimal, natural, and easily recognizable ingredients. Industrial sugar, often perceived as a processed ingredient, may not align with these preferences, affecting product formulation and demand.
- Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: Sugar production, particularly in sugarcane and sugar beet cultivation, can have environmental impacts, such as deforestation, water usage, and soil degradation. Consumers and regulatory bodies are increasingly concerned about sustainable and environmentally responsible practices in sugar production.
- Price Volatility: The price of sugar can be subject to significant fluctuations due to factors like weather conditions, crop yields, and global supply and demand dynamics. This price volatility can create uncertainties for sugar producers and users, impacting their financial planning and profitability.
- Alternative Sweeteners and Sugar Substitutes: The rise of alternative sweeteners, such as stevia, erythritol, and monk fruit, poses a challenge to the industrial sugar market. These natural or artificial sweeteners are gaining popularity as consumers seek sugar-free or lower-calorie options.
- Trade Barriers and Export Challenges: Sugar production is subject to trade restrictions and tariffs in various regions, which can limit market access for producers. Additionally, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact the competitiveness of sugar exports.
Growth rate in industrial sugar market
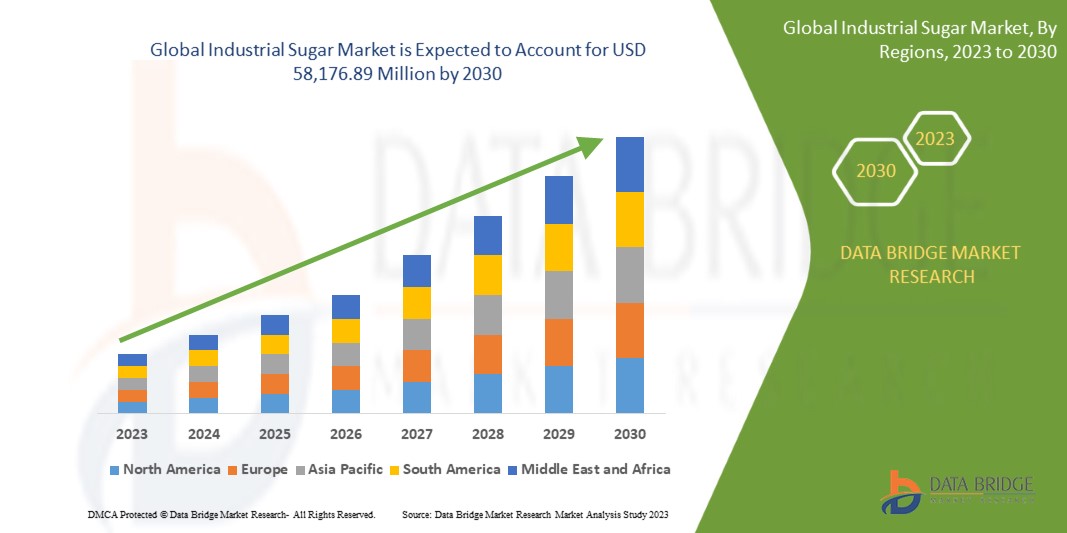
- According to an in-depth analysis conducted by Data Bridge Market Research, the global industrial sugar market is poised for significant growth, with a projected value of USD 58,176.89 million anticipated by the year 2030. This forecast underscores the resilience and enduring importance of the industrial sugar industry on a global scale. The market is expected to exhibit a steady compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.4% during the forecast period, indicating a gradual but substantial expansion.
- Several factors contribute to this projected growth in the industrial sugar market. One of the key drivers is the persistent demand for sugar across various industrial sectors, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and biofuels. Sugar remains an indispensable ingredient in a wide array of products, playing a vital role in enhancing taste, texture, and preservation.
- The global population continues to expand, driving increased consumption of processed foods and beverages, where industrial sugar is a crucial component. As emerging economies witness rising income levels and urbanization, there is a growing appetite for convenience foods and sweetened beverages, further propelling the demand for industrial sugar.
- It’s important to note that the market also faces challenges, including concerns about the health implications of excessive sugar consumption and regulatory measures aimed at reducing sugar intake. Nevertheless, industry stakeholders are actively exploring solutions, such as developing low-sugar and sugar-free alternatives, to address these concerns while maintaining market viability.
Impact of Climate Change on Sugar Production
Climate change has significant and far-reaching effects on sugar production, impacting both the quantity and quality of sugar crops. Here are some key ways in which climate change affects sugar production:
- Shifts in Temperature and Precipitation Patterns: Climate change can alter the traditional temperature and precipitation patterns in sugar-producing regions. Extreme heat waves and prolonged droughts can reduce crop yields and sugar content in sugarcane and sugar beets.
- Water Scarcity: Water scarcity, exacerbated by changing climate conditions, can affect sugar cultivation. Sugarcane and sugar beets require substantial amounts of water, and reduced water availability can lead to lower yields and smaller-sized crops.
- Increased Pest and Disease Pressure: Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns can create favorable conditions for pests and diseases that affect sugar crops. Insect infestations and diseases like sugarcane rust can lead to crop losses.
- Changing Growing Seasons: Climate change can disrupt traditional growing seasons, leading to uncertainty in crop planning and harvesting. Early flowering or delayed maturation can affect crop quality and yields.
- Impact on Sugar Content: Temperature fluctuations and water stress can reduce the sugar content of sugarcane and sugar beets. This has a direct impact on sugar extraction and overall production efficiency.
- Loss of Arable Land: Sea-level rise and increased salinity in coastal regions can make previously arable land unsuitable for sugar cultivation. This displacement can lead to reduced production and the need for new land investments.
- Variability in Crop Quality: Climate-induced stress can lead to variability in crop quality. Inconsistent sugar content and impurities can challenge processing facilities and impact the final product’s quality.
- Economic and Social Impacts: The impacts of climate change on sugar production can have broader economic and social consequences. Reduced yields and lower quality crops can lead to decreased income for farmers and affect employment in the sugar industry.
- Adaptation Strategies: In response to climate change, the sugar industry is adopting various adaptation strategies. These include developing drought-resistant sugarcane varieties, improving irrigation practices, and investing in more efficient processing technologies.
- Sustainable Practices: Some sugar producers are implementing sustainable farming practices, such as organic and regenerative agriculture, to mitigate the environmental impacts of climate change and improve resilience.
To gain more knowledge about market visit
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-industrial-sugar-market
About Us
Data Bridge Market Research provides global coverage, offering insights into markets and industries across the world. This global perspective is valuable for businesses and investors looking to expand their operations internationally.
Data Bridge Market Research often participates in industry events, conferences, and webinars, where they share their expertise and insights on market trends and developments.